100. Same Tree
Given the roots of two binary trees p and q, write a function to check if they are the same or not.
Two binary trees are considered the same if they are structurally identical, and the nodes have the same value.
Example 1
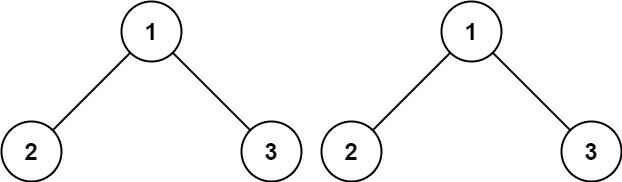
Input: p = [1,2,3], q = [1,2,3]
Output: true
Example 2
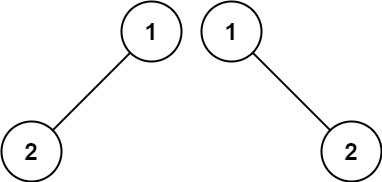
Input: p = [1,2], q = [1,null,2]
Output: false
Example 3
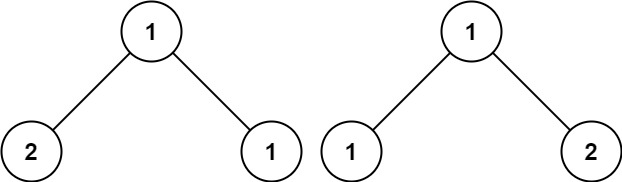
Input: p = [1,2,1], q = [1,1,2]
Output: false
Constraints
- The number of nodes in both trees is in the range [0, 100]
- -104 <= Node.val <= 104
솔루션
1. 첫 번째 솔루션: BFS + 문자열 비교
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
var isSameTree = function(p, q) {
const pTraverse = bfs(p);
const qTraverse = bfs(q);
return pTraverse.toString() === qTraverse.toString();
};
const bfs = (node) => {
const result = [];
if (!node) return result;
const queue = [node];
while(queue.length) {
const selectedNode = queue.shift();
result.push(selectedNode === null ? null : selectedNode.val);
if (selectedNode) {
queue.push(selectedNode.left || null);
queue.push(selectedNode.right || null);
}
}
return result;
};
시간 복잡도
모든 노드를 한 번씩 방문하므로 O(N)
공간 복잡도
마지막 레벨에서 최대 노드 수는 약 N/2이고, 이를 큐와 배열로 저장하므로 O(N)
단점
- 불필요한 메모리 사용: 전체 구조를 배열에 저장하므로 공간 낭비가 큼
- null 처리의 복잡성: null을 명시적으로 넣어야 구조 비교가 정확함
- 문자열 비교의 불안정성: 구조가 다름에도 문자열이 유사하게 보일 수 있음
bfs(p) => [1, 2, null]
bfs(q) => [1, null, 2]
bfs(p).toString() === '1,2,'
bfs(q).toString() === '1,,2'
// → 다르게 나오므로 이 예시는 문제 없음. 그러나 구조 유사성이 높을 경우 혼동 가능
2. 두 번째 솔루션: DFS 기반 재귀 방식
var isSameTree = function(p, q) {
if (!p && !q) return true;
if (!p || !q) return false;
if (p.val !== q.val) return false;
return isSameTree(p.left, q.left) && isSameTree(p.right, q.right);
};
시간 복잡도
O(N)
공간 복잡도
O(h), 트리 높이만큼의 재귀 스택 사용
장점
- 별도 배열 저장 없이 스택만 사용
- 간결하고 읽기 쉬운 코드
- null, 값 비교, 구조 비교를 한 번에 처리
3. 세 번째 솔루션: 개선된 BFS 방식
var isSameTree = function(p, q) {
const queue = [[p, q]];
while (queue.length > 0) {
const [node1, node2] = queue.shift();
if (!node1 && !node2) continue;
if (!node1 || !node2) return false;
if (node1.val !== node2.val) return false;
queue.push([node1.left, node2.left]);
queue.push([node1.right, node2.right]);
}
return true;
};
개선점
- 노드 쌍을 큐에 저장하여 구조 및 값 비교를 동시에 처리
- 값이 다를 경우 즉시 종료 (early return)
BFS vs DFS 비교
1. 공간 복잡도
- DFS는 트리를 수직으로 탐색하므로 최대 깊이 h만큼의 스택만 필요 (O(h))
- BFS는 트리를 수평으로 탐색하므로 가장 넓은 층의 너비만큼 큐가 필요 (O(N))
2. BFS가 유리한 경우
- 트리 깊이가 깊어 스택 오버플로우 위험이 있는 경우
- 디버깅 시 구조 순서대로 비교 및 로깅이 필요한 경우
예시
BFS는 ROOT → LEFT → RIGHT 순서로 탐색되기 때문에, 사람이 보기 쉽고 레벨별 로깅에 적합하다.
Comparing: 1 vs 1
Comparing: 2 vs 2
Comparing: 3 vs 3
...
'Web Development > algorithm' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Algorithm][LeetCode 1920] buildArray (0) | 2025.05.06 |
|---|---|
| [Algorithm][LeetCode 101] Symmetric Tree (0) | 2025.05.05 |
| [Algorithm][LeetCode 96] Unique Binary Search Trees (1) | 2025.05.03 |
| [Algorithm][LeetCode 2962] Count Subarrays Where Max Element Appears at Least K Times (0) | 2025.04.30 |
| [Algorithm][LeetCode 560] Subarray Sum Equals K 문제 풀이 - 누적합과 Hash Map 활용법 (1) | 2025.04.27 |
